“ଓଡ଼ିଆ ଭାରି ବଢିଆ, ତେଣୁ ଆସ ଶିଖିବା ଓଡ଼ିଆ”
Odia Bhari Badhia, Tennu Asa Sikhiba Odia
WHY STUDY ODIA ?
Odia is the predominant language of the Indian State of Odisha where native Speakers comprise 80% of population. It is also spoken in parts of West Bengal, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the 22 scheduled languages.
Odia is the official language of Odisha and the second official language of Jharkhand.
Odia is also an Indian Classical Language along with Sanskrit, Tamil, Telugu, Kannada and Malayalam. It is the first language from Indo-Aryan linguistic group to be billed in the list of Classical language on the basis of having a long literary history and not having borrowed extensively from other languages.
The script of modern Odia is a development of the Kalinga script. The rounded appearance of the alphabets reveals key features of the Odia script. This appearance was largely due to the ancient practice of writing manuscripts on palm leaves that has a tendency to tear if too many straight lines were used on the surface.


Important facts about Odia
Pronunciation: Odia; previously pronounced as Oriya
Native: India
Region: Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal and Andhra Pradesh
Speakers: Around 38 million in the following Indian States:
- Odisha -35,400,000
- Chhattisgarh – 950,000
- Jharkhand – 543,000
- Andhra Pradesh – 390,000
- Assam – 268,000
- West Bengal – 216,000
- Gujarat – 142,000
Dialects: Ethnologue identifies a number of regional varieties of Oriya:
- Halbi
- Midnapore Oriya
- Mughalbandi (Standard Oriya)
- North Balasore Oriya
- Northwestern Oriya
- Southern Oriya
- Western Oriya
ABOUT ODISHA
Odisha, one of the 29th states of India, located at the country’s eastern coast was constituted on April 1, 1936 as the first Indian state (pre-independence) on linguistic basis constituting predominantly of Odia-speaking regions. It is the 9th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. It is also the 3rd most populous state of India in terms of tribal population with 62 culturally vibrant tribes including 13 primitive tribal groups.
In terms of history, Odisha is the heartland of ancient and powerful kingdoms as Kalinga, Utkal, Odra & Kosala. It is here only Emperor Ashoka renounced violence, embraced Buddhism and became Dharmasoka from Chandasoka after the Kalinga war. Through vast maritime trade route of Kalinga, Emperor Ashoka propagated Buddhism and made it a world religion.
Odisha is surrounded by West-Bengal on the north-east, Jharkhand on the north, Chhatishgarh on the west and Andhra Pradesh on the south-west while the Bay of Bengal washes its shores on the south east. The state of Odisha extends from 17.49N latitude to 22.34N latitude and from 81.27E longitude to 87.29E longitude. The state has an area of 155,707 km2 and extends for 1030 km from north to south and 500 km from east to west. Its coastline is 485 km long. The state is divided into 30 districts which are further subdivided into 314 blocks.
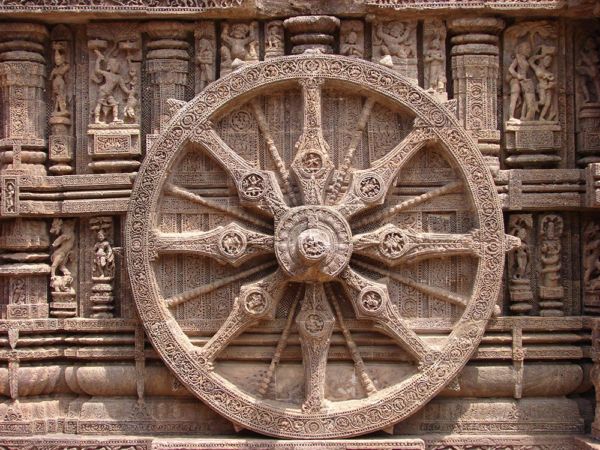
Odisha, known as the Soul of India, has always enthralled visitors with its eternal mystical charm, a beautiful poetic cocktail of history, culture and nature. With the vanishing sea of Chandipur in the North, the architectural marvel of Ratnagiri, the mysticism of Lord Jagannath, the majestic Konark Sun Temple, the dazzling Chilika Lake and the freezing Daringbadi in the tribal hills of the South, Odisha has always been a connoisseur’s delight.
Through centuries Odisha has retained its cultural identity within the mainstream of pan-Indian culture. It has a distinct tradition of painting, architecture, sculptures, handicrafts, handlooms, music and dance. Architecture in Odisha has found its supreme expression in the form of temples, some of which are among the finest in the world. Of these three are most famous: the Lingaraj Temple at Bhubaneswar (11th century A.D.), the Jagannath Temple at Puri (12th century A.D.) and the great Sun Temple at Konark (13th century A.D.).
Today Odisha is one of the fastest growing States in India with growth rate above the national average. The state capital Bhubaneswar is the First City to be declared a ‘Smart City’ by the Union Government’s Urban Development Ministry out of the list of 20 cities across India.


WHAT IS THE SCOPE AFTER LEARNING ODIA ?
The world is becoming more and more connected and the demand for Odia specialists in India is growing. After learning Odia you can find openings in various sectors like language specialist. It helps you to convey thoughts and emotions with native Odia people.
Odia is widely used as medium of communication in Odisha including govt offices, work places, courts, hospitals, institutions and markets.
Hence, it becomes imperative for students from outside to get acquainted with the language if they want to pursue a career here in the state or even want to settle here.
Similarly, the language plays an important criteria in different state exams in Odisha including administrative services, staff selection etc. And since past years, it has been seen more and more students from KIIT going for administrative exams, so this course can help them to brush up their language paper.
Apart from this, the course will make the students competent enough to minimum read and write simple sentences in Odia which shall help them to have a comfortable communication like public interaction.
You will gain more knowledge about prominent writers of Odisha who have received awards in various spheres like-Gyanapitha awardee name is Padmashree Sachi Routray, Gopinatha Mohanty, Sitakanta Mohapatra, Pratibha Ray etc.Novelist –Fakir Mohan Senapati, Gopal bhalav Das, KahnucharanMohanti, Gopinatha Mohanty,Prativa Ray; Poets-RamakantaRatha,JayantaMohapatra; Freedom fighter- Subhash Chandra Bose, Bira Surendra Sai, Utkalmani Gopabandhu Das and many more aspects.

WHAT DOES THE ODIA (BEGINNER) COURSE OFFERS?

Course Objectives :
- To enable students to make interactions in simple basic Odia and to make them read and write simple Odia.
- To help students improve their proficiency in all areas of Odia language including listening, speaking, reading and writing.
Course Outcomes :
- Will be able to demonstrate an elementary knowledge of Odia sentence structure through speaking and writing in Odia scripts
- Will be able to pronounce basic Odia reasonably.
- Will be acquainted with the basic Odia customs and Culture.
Course Details (Syllabus)
Course Structure
- Medium of instruction Odia
- Hindi & English
- Numbers of hours ; 30 hours
- Number of lessons per week: 4
- Duration of the course:3 months
- Course Fees: Rs. 5000/-
Mode of Evaluation
- Mode of Evaluation
- Written test-50
- Speaking-30
- Listening-10
- Reading-10
- Total-100 marks
Unit-1 –A study of Applied Odia Grammar (10 Hours)
- Alphabet
- Vowel & Consonant
- Question words
- Personal pronouns in all cases
- Symbols
- Word making
- Sentence formation
- Phrase
- Noun Phrase
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Phrase
- Clause
- Noun Clause
- Adjective Clause
- Adverbial Clause
- Sub Clause
Unit 2-Vocabulary (8 Hours)
- Effective Communication in Odia
- Listening Vocabulary-This will include the Odia words we hear and how we comprehend.
- Speaking Vocabulary –This will include how to speak Odia words.
- Reading Vocabulary-This will include how to read Odia words.
- Numbers in Odia from 0 to 100
Unit 3-Communicative Skill (8 Hours)
- How to greet
- Locating objects and place
- How to ask and answer questions
- How to introduce oneself
- How to talk about the legend person
- How to talk over the telephone
Unit 4-Civilisation (4 Hours)
- Festivals
- Wildlife
- Monuments
- Handicrafts
- Tribal culture
- Performing arts-Music, Dance, Odia cinema etc.
- Odia cuisine.
- Odisha customs and traditions

